|
 Inspection: Inspection:
The foot
is deformed turned inside. The external edge is convex,
turned to the bottom, the skin is lengthened. The internal
edge is concave, the skin is short. There are many furrows.
A midtarsal lateral internal furrow , very marked, which
continues with a plantar midtarsal furrow, a furrow under
the internal tibia malleolus and a posterior furrow over the
calcaneum.


Right
clubfoot.
 Palpation:
Palpation:
The large
tuberosity of the calcaneum is climbed. Abnormal osseous
projections are found on the top of the foot (ankle bone
head and calcaneum large apophysis joint), adduction in the
Lisfranc joint. Bot, ligaments, aponevrotic and muscular
retractions are found with palpation. Sometimes there are
cutaneous adherences on the internal face. The varus muscles
(which bring the foot inside) are active and shortened, the
valgus muscles (which bring the foot outwards) are
inhibited.
 Evaluations
grids of: A DIMEGLIO In Montpellier: Evaluations
grids of: A DIMEGLIO In Montpellier:
http://www.afcp.com.fr/res121103/pbve/pbve_descript.html
 Inutero
echographies right foot normal, left foot presenting a
clubfoot: Inutero
echographies right foot normal, left foot presenting a
clubfoot:

4
months

5
months

6
months
 Radiological examination:
Radiological examination:
1
 2
2

1- Radio
of a normal foot (two years-old child).
2- Radio
of a bilateral clubfoot: face and in load (two years-old
child).
 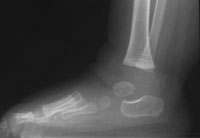
Radios of
a bilateral clubfoot.: profile and in load (two years-old
child)
1
 2 2

1-Radio of
a clubfoot varus equine (seven years-old child).
2-Radio of
a normal foot (seven years-old child).

In load
radio showing a bad result.

Face radio
of a right clubfoot and a normal left foot (seven years-old
child).
 Note: Note:
Contrary
to generally accepted ideas, the long and fine feet are
difficult to treat. They are laxes and we can easily obtain
a false correction in the saggital plan of the median tarsus
articulation.
|